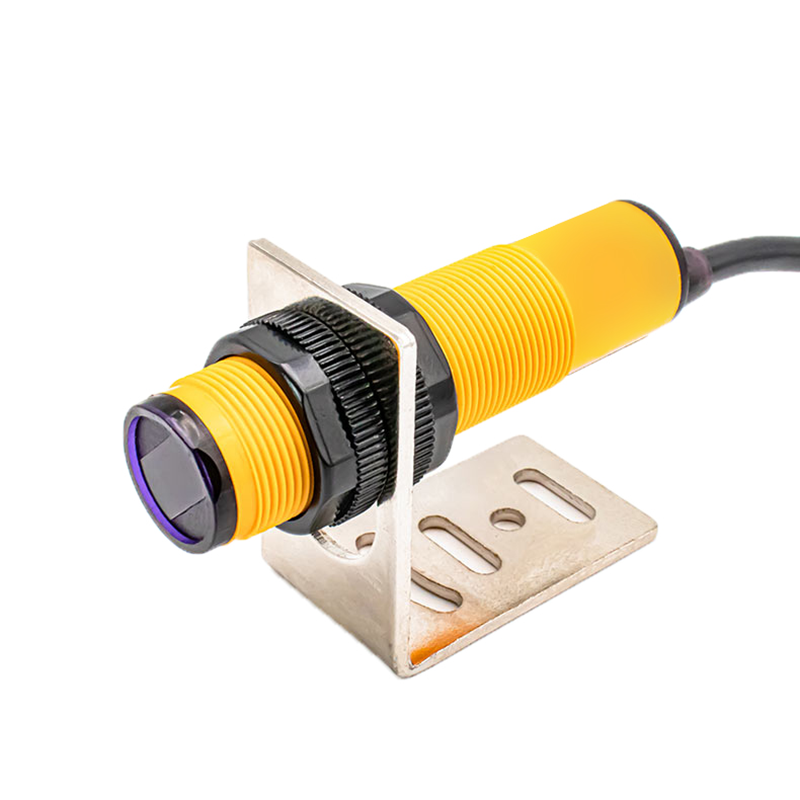
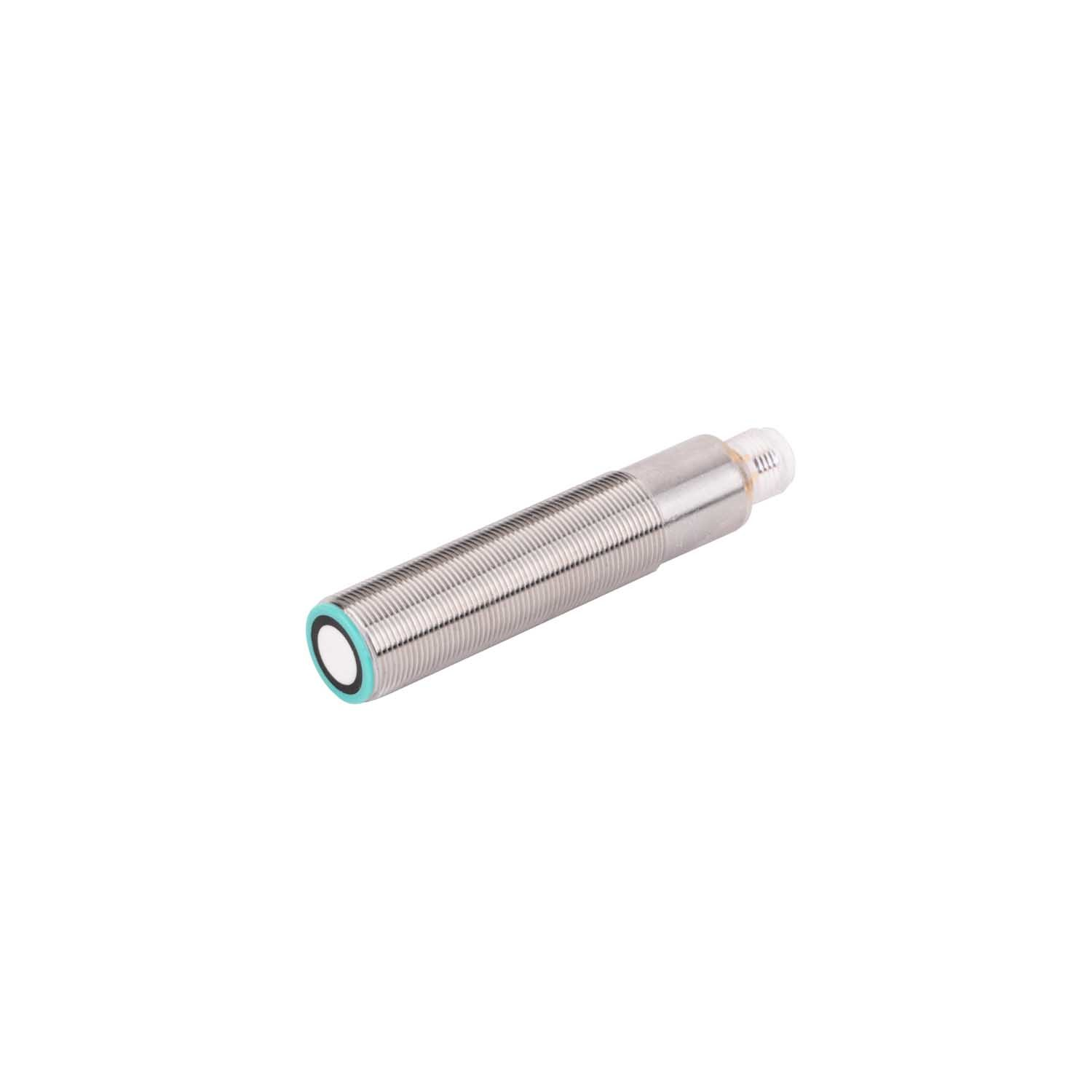
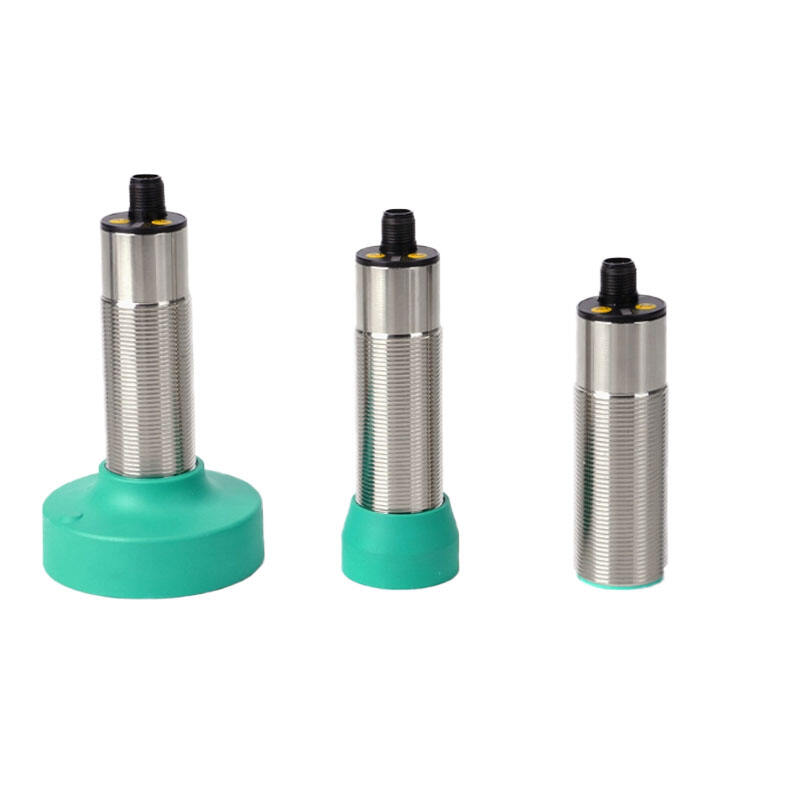
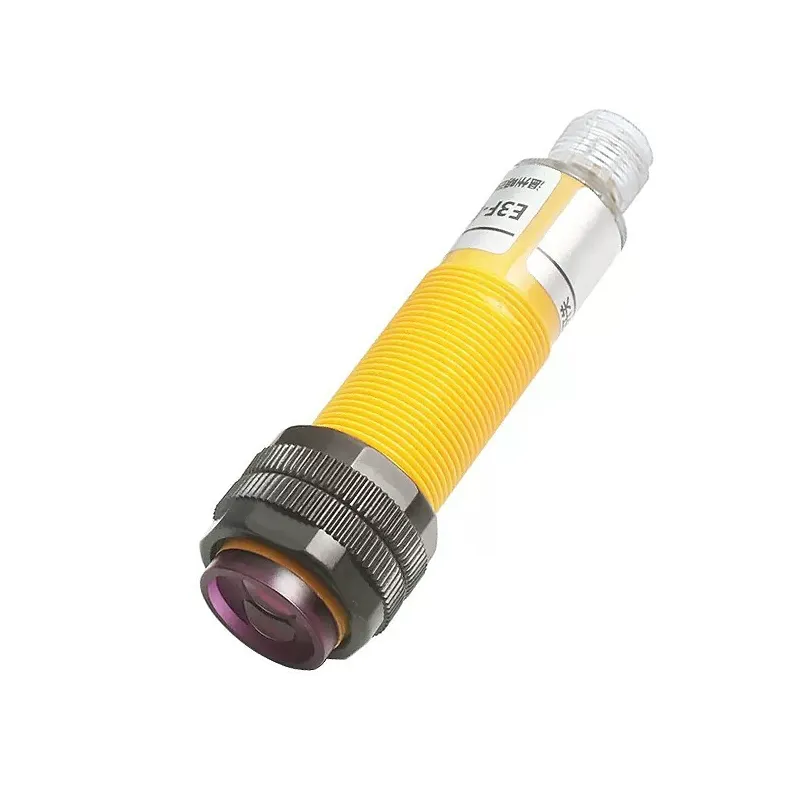
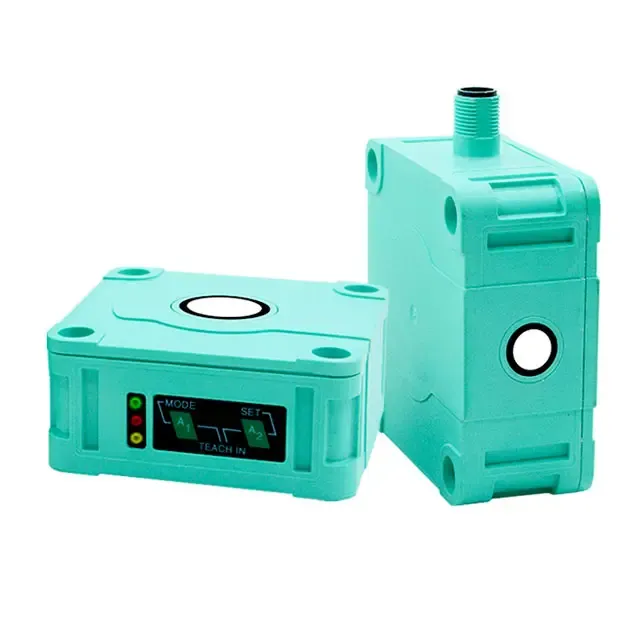
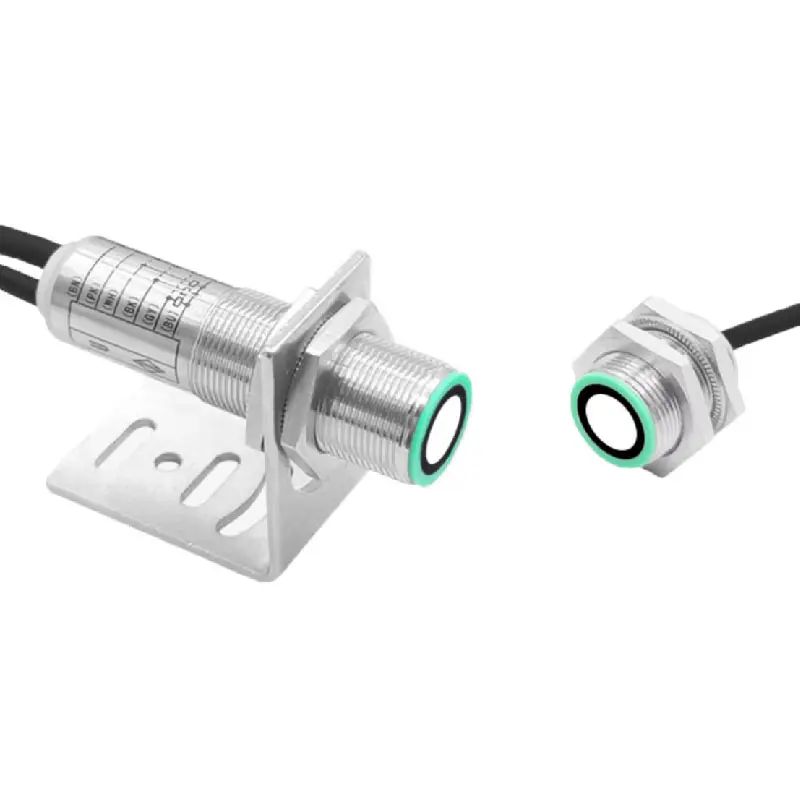
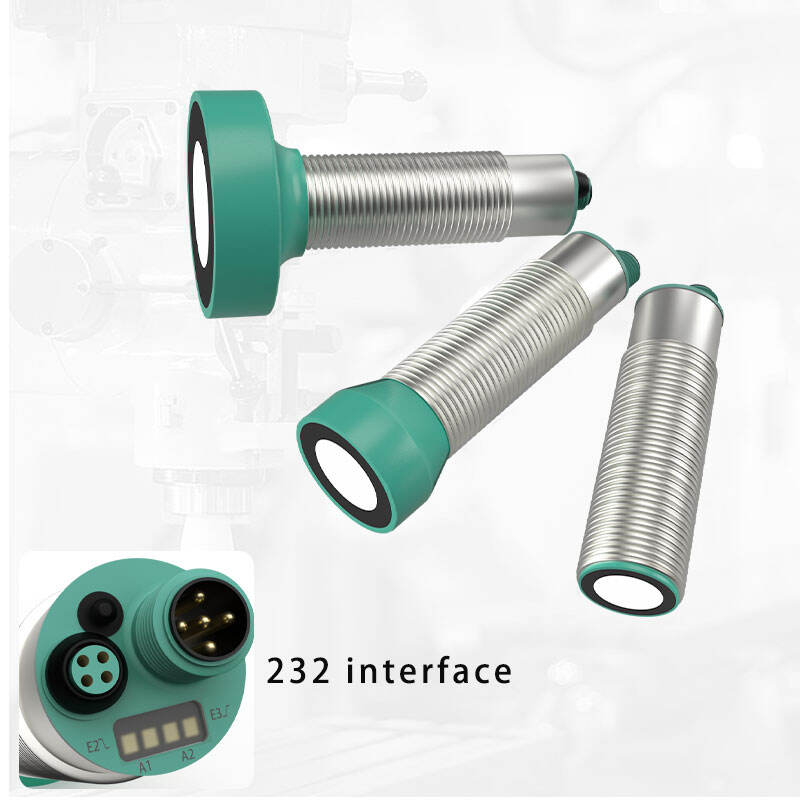
photoelectric sensor working
A photoelectric sensor represents a sophisticated detection device that operates on the principle of light emission and reception. This advanced technology utilizes a light beam, typically infrared, visible red, or laser, to detect the presence, absence, or distance of objects. The sensor consists of two main components: an emitter that projects the light beam and a receiver that detects the reflected or interrupted light signal. When an object enters the sensor's detection zone, it either blocks or reflects the light beam, triggering a response from the sensor. Modern photoelectric sensors incorporate various sensing modes, including through-beam, retro-reflective, and diffuse reflection, making them incredibly versatile for different applications. These sensors excel in industrial automation, manufacturing processes, packaging lines, and security systems. Their high-speed response time, typically in milliseconds, enables precise detection and counting of fast-moving objects. Additionally, the sensors can operate effectively in challenging environments, featuring built-in protection against ambient light interference and environmental factors. The integration capabilities with modern control systems through digital or analog outputs make them essential components in smart manufacturing and Industry 4.0 applications.